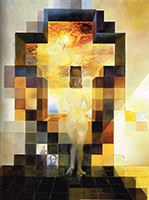Post-World War II
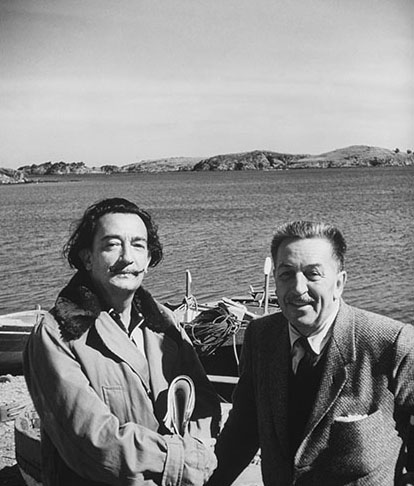

In 1946 Dalí worked with Walt Disney and animator John Hench on an unfinished animated film, Destino.
Dalí exhibited new work at the Bignou Gallery from November 1947 to January 1948. The 14 oil paintings and other works in the exhibition reflected Dalí's increasing interest in atomic physics. Notable works included Dematerialization Near the Nose of Nero (The Separation of the Atom), Intra-Atomic Equilibrium of a Swan's Feather, and a study for Leda Atomica. The proportions of the latter work were worked out in collaboration with a mathematician.
In early 1948 Dalí's 50 Secrets of Magic Craftsmanship was published. The book was a mixture of practical advice on painting, and anecdotes and Dalínian polemics.
In 1948 Dalí and Gala moved back into their house in Port Lligat, on the coast near Cadaqués. For the next three decades they would spend most of their time there, spending winters in Paris and New York. Dalí 's decision to live in Spain under Franco and his public support for the regime prompted outrage from many anti-Francoist artists and intellectuals. Pablo Picasso refused to mention Dalí's name or acknowledge his existence for the rest of his life. In 1960, André Breton unsuccessfully fought against the inclusion of Dalí's Sistine Madonna in the Surrealist Intrusion in the Enchanter's Domain exhibition organized by Marcel Duchamp in New York. Breton and other Surrealists issued a tract to coincide with the exhibition denouncing Dalí as "the ex-apologist of Hitler... and friend of Franco."

In December 1949 Dalí's sister Anna Maria published her book, Salvador Dalí Seen by his Sister. Dalí was angered by passages which he considered derogatory towards his wife Gala and broke off relations with his family. When Dalí's father died in September 1950 Dalí learned that he had been virtually disinherited in his will. A two-year legal dispute followed over paintings and drawings Dalí had left in his family home, during which Dalí was accused of assaulting a public notary.
As Dalí moved further towards embracing Catholicism he introduced more religious iconography and themes in his painting. In 1949 he painted a study for The Madonna of Port Lligat (first version, 1949) and showed it to Pope Pius XII during an audience arranged to discuss Dalí 's marriage to Gala. This work was a precursor to the phase Dalí dubbed "Nuclear Mysticism," a fusion of Einsteinian physics, classicism and Catholic mysticism. In paintings such as The Madonna of Port Lligat, The Christ of Saint John on the Cross and The Disintegration of the Persistence of Memory, Dalí sought to synthesize Christian iconography with images of material disintegration inspired by nuclear physics. His later Nuclear Mysticism works included La Gare de Perpignan (1965) and The Hallucinogenic Toreador (1968–70).

Dalí's keen interest in natural science and mathematics was further manifested by the proliferation of images of DNA and rhinoceros horn shapes in works from the mid-1950s. According to Dalí, the rhinoceros horn signifies divine geometry because it grows in a logarithmic spiral. Dalí was also fascinated by the tesseract (a four-dimensional cube), using it, for example, in Crucifixion (Corpus Hypercubus).
Dalí had been extensively using optical illusions such as double images, anamorphosis, negative space, visual puns and trompe l'œil since his Surrealist period and this continued in his later work. At some point, Dalí had a glass floor installed in a room near his studio in Port Lligat. He made extensive use of it to study foreshortening, both from above and from below, incorporating dramatic perspectives of figures and objects into his paintings. He also experimented with the bulletist technique pointillism, enlarged half-tone dot grids and stereoscopic images. He was among the first artists to employ holography in an artistic manner. In Dalí's later years, young artists such as Andy Warhol proclaimed him an important influence on pop art.
In 1960, Dalí began work on his Theatre-Museum in his home town of Figueres. It was his largest single project and a main focus of his energy through to 1974, when it opened. He continued to make additions through the mid-1980s.
In 1968, Dalí bought a castle in Púbol for Gala, and from 1971 she would retreat there for weeks at a time, Dalí having agreed not to visit without her written permission. His fears of abandonment and estrangement from his longtime artistic muse contributed to depression and failing health.
In 1980, at age 76, Dalí's health deteriorated sharply and he was treated for depression, drug addiction and Parkinson-like symptoms, including a severe tremor in his right arm. There were also allegations that Gala had been supplying Dalí with pharmaceuticals from her own prescriptions.
Gala died on June 10th, 1982, at the age of 87. After her death, Dalí moved from Figueres to the castle in Púbol, where she was entombed. Then, in May 1983, what was said to be Dalí's last painting, The Swallow's Tail, was revealed. The work was heavily influenced by the mathematical catastrophe theory of René Thom. However, some critics have questioned how Dalí could have executed a painting with such precision given the severe tremor in his painting arm.

From early 1984 Dalí's depression worsened and he refused food, leading to severe undernourishment. Dalí had previously stated his intention to put himself into a state of suspended animation as he had read that some microorganisms could do. In August 1984 a fire broke out in Dalí's bedroom and he was hospitalized with severe burns. Two judicial inquiries found that the fire was caused by an electrical fault and no findings of negligence were made. After his release from hospital Dalí moved to the Torre Galatea, an annex to the Dalí Theatre-Museum
In November 1988, Dalí entered hospital with heart failure. On December 5th, 1988, he was visited by King Juan Carlos, who confessed that he had always been a serious devotee of Dalí. Dalí gave the king a drawing, Head of Europa, which would turn out to be Dalí's final drawing. Then on the morning of January 23rd, 1989, while his favorite record of Tristan and Isolde played, Dalí died of heart failure at the age of 84. He is buried in the crypt below the stage of his Theatre-Museum in Figueres. The location is across the street from the church of Sant Pere, where he had his baptism, first communion, and funeral, and is only 450 metres (1,480 ft) from the house where he was born.